We should carefully look after trees to ensure they grow well. For young trees, we need to provide irrigation and fertilising for early growth, give them support by staking, control weeds around them and carry out formative pruning to create a balanced and healthy tree form, which could help reduce the tree risk in the future. For mature trees, we need to be more aware of potential risk and carry out inspection by trained personnel, especially in areas where there are greater numbers of people and traffic.
We can all take care of trees in the community and make Hong Kong a greener place. Below are some practical tips:
Practical Tips on Tree Care
Provide a suitable growing environment for trees

To allow adequate space for future growth both above and below ground

To keep a suitable distance between trees and buildings

To regularly prune tree crowns and remove dead / broken branch
To monitor the health conditions of trees in our community
Tree Protection Measures
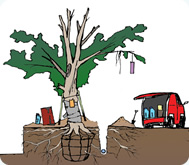
- Do not excavate near tree roots
- Do not step on tree roots
- Do not place or store heavy objects near trees (including no parking near trees)
- Do not place liquids such as chemicals near trees
- Do not damage tree bark (including no graffitii or bark removal)
- Do not hang nor attach items on trees permanently
- Pictorial Guide for Tree Maintenance
Tree Care During Construction

Do not place tools around trees

Do not girdle trees

Do not use trees as anchors

Do not truncate tree roots

Do not top trees

Do not fix any objects onto tree trunks

Do not conduct any works within the tree protection zone

Do not work with machines near trees
Tree Management Practice Notes
- Tree Management Practice Note No.1: Tree Preservation during Construction
- Tree Management Practice Note No.2: Key Steps in Tree Risk Management in Private Properties
- Tree Management Practice Note No.3: Tree Pruning
- Tree Management Practice Note No.4: Management of Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Tree
- Guidelines on Arboriculture Occupational Safety and Health
- Guideline on Pavement Renovation Works and Tree Stability
- Guideline on Tree Stump Treatment
- Management Guidelines for Stonewall Trees
- Guidelines on Tree Transplanting
- Guidelines on Tree Pruning
- Management Guidelines for Mature Trees
- Guidelines on Tree Preservation during Development
- Note on Common Wood Decay Fungi on Urban Trees of Hong Kong
- Tree Removal - A difficult but rational decision (Chinese only)
- BRRD disease can be spread through root contact, contaminated soil, ground water, surface water, and even through the air.
- The public are strongly advised to stay away from known infected trees as contaminated soil on shoes can also spread the disease.
- It is an international disease prevalent in tropical and sub-tropical regions with no effective cure. There have been numerous claims of cures or effective management, but once the tree is infected, it cannot be cured.
- BRRD disease can lead to swift deterioration in health of the tree, causing eventual decay and irreversible structural damage to tree roots, posing a serious threat to public safety.
- BRRD disease has devastating impact on our landscape. Once a site is infected, it must be completely disinfected.
- A multi-pronged approach combining preventive and management tactics is being adopted by the Greening, Landscape and Tree Management Section (GLTMS) to safeguard our urban forest assets.
- The Manual on the Management of Brown Root Rot Disease illustrates step-by-step the recommended management approach for BRRD infected trees as well as fundamental steps and key measures that should be implemented in removing BRRD infected trees.
- Tree Management Practice Note No.4: Management of Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Tree
- Video on Proper Removal and Follow-up Procedures of BRRD Infected Tree
- Manual on the Management of Brown Root Rot Disease
- Annex A - Pictorial Guide for Identification of Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Trees
- Annex B to E - for internal use by the Government
- Annex F - Template of Warning Sign for Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Old and Valuable Trees
- Annex G - Checklist for Tools and Equipment and Personal Protection Equipment in the Removal of Brown Root Rot Disease (BRRD) Infected Tree
- Annex H - Template of Warning Sign for Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Tree
- Annex I - Sample Method Statement on Removal of Brown Root Rot Disease Infected Tree
- Once an infected site is known, the focus is to save the surrounding landscape and nearby vegetation.
- International best practice and policy position is to limit the spread to other trees and remove the infected tree as soon as practicable, including other plants within the infection area and the root system of the infected tree.
- The site should be properly disinfected and replanting of trees at the same site is not recommended unless it is proven to be rid of disease pathogen.
- The GLTMS has been collaborating with research institutions to conduct fungal surveys, diagnosis and preventive studies on aspects such as BRRD disease resistant species and cure.
- Research projects and exchange of views with overseas experts can enhance our understanding of the disease, which could help build a more holistic, active and successful management approach in the future.
- To positively build capacity and raise overall professional knowledge and standards in the industry will be the key towards better management of BRRD disease.
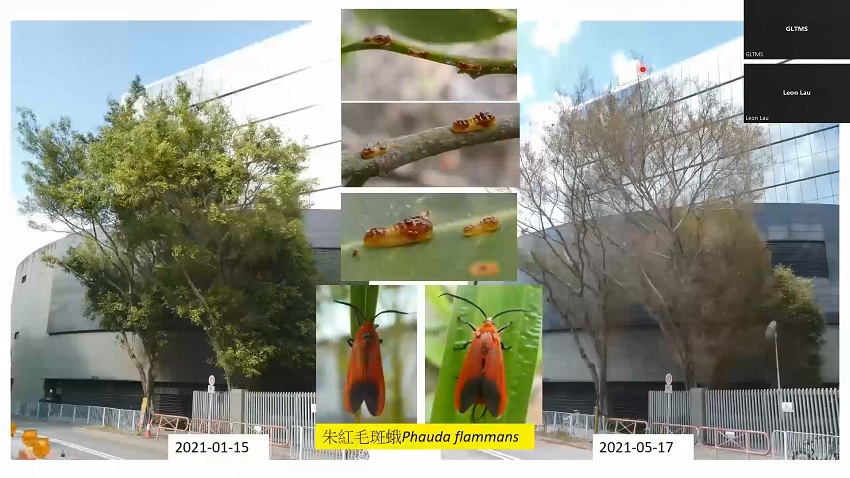
Introduction
Phauda flammans are found in southern China, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia and India. Phauda flammans larvae (larvae) feed on leaves to survive and are commonly found on Ficus trees. After a larva matures, it will form a cocoon, pupate, and then emerge from the pupal case and turn into an adult. The adult will then lay eggs on leaves after mating, which will hatch into larvae and start feeding on leaves. There can be more than two generations of larvae per year.

Egg

Larva

Larva

Pupa

Adult

Adult
Larval infestation
It is a natural phenomenon that larvae feed on leaves of Ficus trees. However, this phenomenon was more apparent in Hong Kong in the summer of 2020. Though the appearance of infested Ficus trees has deteriorated due to defoliation, the infestation did not have a serious impact on their overall health and structural conditions.
Larvae control measures
To ensure the effective implementation of integrated pest management, specific measures should be adopted having regard to different stages of the life cycle of the insect (eggs, larvae, pupae and adults), followed by monitoring, evaluating the effectiveness of the control measures and making adjustments whenever necessary. Private property owners or management personnel can monitor affected trees on their properties on a regular basis, and take appropriate control measures according to the infestation extent of the trees, their surrounding environment, as well as different stages of the life cycle of the insect. Pest control work for trees involves arboricultural knowledge and requires professional input. Private property owners or management companies should engage qualified professionals to advise, supervise and handle all matters in relation to tree work. Appropriate control measures include:
-
To wrap the tree trunk with bamboo/straw mats or hessian bags to catch active larvae on the trunk; and to regularly remove and replace bamboo/straw mats or hessian bags that are drenched, so that the trunk will not be weakened in a humid environment for a long time, which will affect its health and structural conditions.

Wrapping the tree trunk with hessian bags to catch larvae
(photo courtesy of the Leisure and Cultural Services Department (LCSD)) -
To step up the clearance of pupae inside the tree bark, crevices in roots, top soil and fallen leaves when larvae are forming cocoons, so that fewer larvae will emerge as adults in the next stage; and to properly handle yard waste such as dead leaves and pupae to prevent pest transmission due to improper transportation.
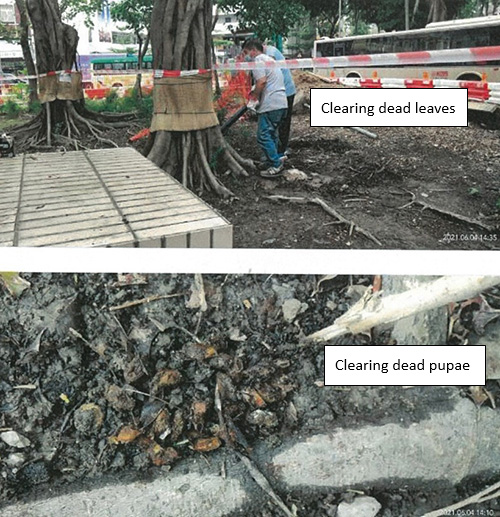

Clearing dead leaves and pupae
(photo courtesy of the LCSD) -
To spray soap water or chilli water on the affected tree crown and tree trunk to remove larvae on the leaves or the trunk.

Spraying soap water
(photo courtesy of the LCSD) -
To consider engaging a professional pest control agent if necessary, as advised by the qualified arboricultural professionals, for pest prevention and control work, particularly the application of agricultural pesticides*.
(*Note: Since pesticides will cause environmental pollution, priority should be given to other methods in preventing and controlling plant pests, and appropriate pesticides should only be used after all other methods have been found ineffective. As regards pesticide application, appropriate pesticides that are the safest, most effective with lower toxicity and approved under the Hong Kong legislation should be used to reduce their impact on the environment and ecology. After applying pesticides, relevant warning signs should be displayed conspicuously. For more information on the safe and proper use of pesticides, please visit the webpage of the Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department at:
https://www.afcd.gov.hk/english/quarantine/qua_pesticide/qua_pes_safe/qua_pes_safe.html )
Warning sign
(photo courtesy of the LCSD)
